Podiatrist
Understanding the Role of a Podiatrist: Specializing in Foot and Ankle Health
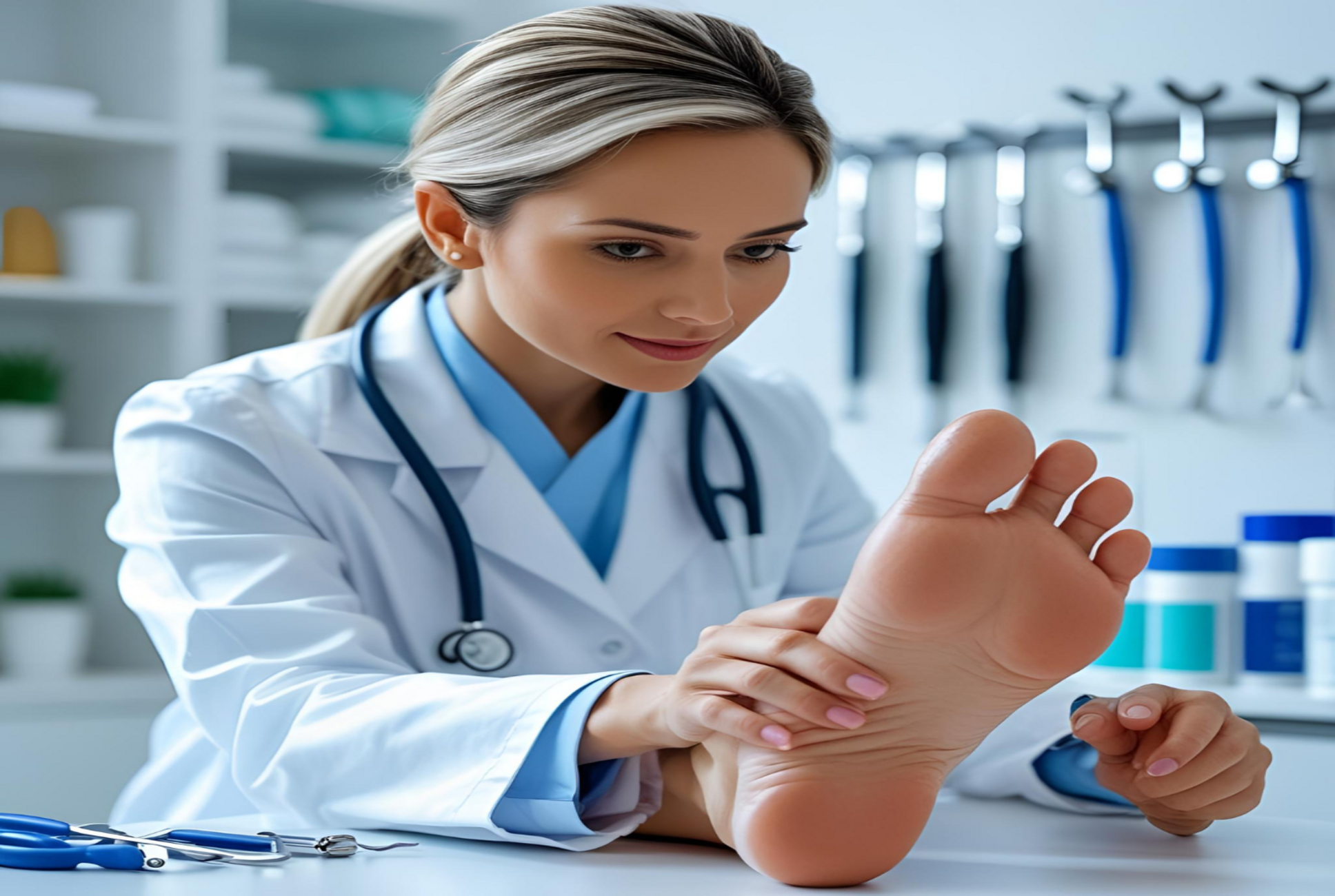
Podiatrist is a specialized field of healthcare focused on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of conditions affecting the feet, ankles, and lower extremities. A podiatrist is a medical professional who specializes in this area and plays a crucial role in helping individuals maintain mobility and overall health. Given that the feet and ankles bear the weight of the body and are vital to mobility, podiatrists play a key role in managing a wide range of medical conditions, injuries, and diseases that affect these parts of the body.
What is a Podiatrist?
A podiatrist is a healthcare professional trained in the medical and surgical care of the feet and lower extremities. The profession encompasses a broad range of duties, including diagnosing and treating conditions, performing surgery, and prescribing medication. Podiatrists work with patients of all ages, from children to the elderly, and their expertise spans from routine care to complex surgeries.
Podiatrists are often consulted when a person experiences foot pain, difficulty walking, or injuries. However, they also treat a variety of chronic conditions that can affect overall health, such as diabetes, arthritis, and vascular diseases.
The Role and Responsibilities of a Podiatrist
Podiatrists diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions that impact the feet and lower extremities. Their role is vital in not only providing direct care but also educating patients on the importance of foot health and providing preventative measures to avoid complications in the future. Here are the primary responsibilities of a podiatrist:
1. Diagnosis and Treatment of Foot and Ankle Conditions
Podiatrists are skilled in diagnosing conditions based on patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Some of the conditions they commonly treat include:
- Injuries: Fractures, sprains, strains, and tendonitis are common foot and ankle injuries that podiatrists treat. They may use imaging tests such as X-rays to evaluate the extent of the injury and recommend treatment options like splints, casts, or surgical intervention when necessary.
- Bunions: A bunion is a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of the big toe. It can cause pain, swelling, and difficulty walking. Podiatrists can recommend treatment options, including custom orthotics, exercises, and surgery if needed.
- Plantar Fasciitis: This condition is characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a band of tissue that runs across the bottom of the foot. Podiatrists can help manage this condition through stretching exercises, physical therapy, and appropriate footwear.
- Flat Feet (Pes Planus): Flat feet occur when the arches of the feet collapse, causing the feet to roll inward. This can lead to pain and discomfort in the feet, legs, and lower back. Podiatrists treat flat feet through orthotic devices, custom insoles, and lifestyle modifications.
- Diabetic Foot Care: People with diabetes are at risk of developing foot problems due to poor circulation and nerve damage (neuropathy). Podiatrists regularly monitor the feet of diabetic patients, treating sores, ulcers, and infections, as well as advising on proper foot hygiene to prevent complications like amputations.
- Athlete’s Foot: This fungal infection affects the skin of the feet and is highly contagious. Podiatrists diagnose and treat athlete’s foot through antifungal medications and advice on preventing its spread.
- Ingrown Toenails: Ingrown toenails occur when the edges of the nails grow into the surrounding skin, causing pain, swelling, and infection. A podiatrist can help treat this condition by removing the nail or recommending proper nail care.
- Corns and Calluses: These thickened areas of skin develop as a result of friction or pressure. Podiatrists can remove corns and calluses safely and provide advice on proper footwear to prevent them from recurring.
2. Surgical Interventions
In some cases, conditions that affect the feet or ankles may require surgical intervention. Some examples of podiatric surgeries include:
- Bunionectomy: A surgical procedure to remove a bunion and realign the toe joint.
- Achilles Tendon Surgery: In cases of severe Achilles tendonitis or ruptures, podiatrists may perform surgery to repair the tendon and restore functionality.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat joint issues in the foot and ankle by making small incisions and using a camera to guide the treatment.
- Toe and Foot Reconstruction: This may be necessary in cases of trauma or congenital deformities where the foot needs to be rebuilt or realigned to improve function and appearance.
3. Preventative Care and Education
Podiatrists emphasize the importance of preventative care, educating patients about proper foot hygiene, suitable footwear, and lifestyle changes to prevent future foot problems. They also help people maintain healthy feet through routine check-ups, especially for individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes. Prevention-focused advice may include:
- Footwear Recommendations: Podiatrists advise on choosing proper footwear based on the patient’s foot structure, activity level, and specific conditions. This includes recommending orthotic insoles or custom-made shoes for people with flat feet, arthritis, or diabetes.
- Exercise and Stretching: Proper exercises can help prevent foot and ankle injuries. Podiatrists often guide patients in stretching and strengthening exercises for the feet and ankles to prevent conditions like plantar fasciitis and tendonitis.
- Nail and Skin Care: People with conditions such as diabetes are more susceptible to foot infections. Podiatrists educate patients on the proper care of their toenails and skin, including how to trim nails correctly, how to avoid cutting too close, and the importance of moisturizing the feet to prevent cracks and dry skin.
- Weight Management: Excess weight can put undue stress on the feet and ankles, leading to problems like arthritis, flat feet, and bunions. Podiatrists may provide advice on maintaining a healthy weight to reduce foot stress.
4. Collaboration with Other Healthcare Providers
Podiatrists work alongside other healthcare providers, including primary care doctors, orthopedists, and physical therapists, to ensure comprehensive care for patients. For example, podiatrists often collaborate with diabetologists to monitor and treat diabetic foot conditions, or with orthopedic surgeons to manage joint conditions and rehabilitation.
Conditions Commonly Treated by Podiatrists
Podiatrists treat a wide variety of foot and ankle conditions. Some of the most common conditions include:
- Plantar Fasciitis: A common cause of heel pain due to inflammation of the plantar fascia ligament.
- Bunions: Painful bumps on the big toe joint caused by misalignment of the bones.
- Hammertoes: A deformity where a toe bends downward, often caused by wearing tight shoes or imbalance in muscle strength.
- Achilles Tendonitis: Inflammation of the Achilles tendon caused by overuse or strain.
- Flat Feet: A condition where the arches of the feet collapse, leading to pain and difficulty walking.
- Gout: A form of arthritis that affects the joints, especially the big toe, causing pain and swelling.
- Fungal Infections: Such as athlete’s foot and toenail fungus, which are treated with antifungal medications and lifestyle changes.
Becoming a Podiatrist
Becoming a podiatrist requires extensive education and training. The steps to become a podiatrist include:
- Undergraduate Education: Aspiring podiatrists typically complete a bachelor’s degree with a focus on biology, chemistry, or other science-related fields.
- Podiatric Medical School: After earning a bachelor’s degree, prospective podiatrists attend a podiatric medical school for four years. The first two years focus on basic medical sciences, while the final two years are dedicated to clinical rotations, where students gain hands-on experience in diagnosing and treating patients.
- Residency: After graduating from podiatric medical school, podiatrists must complete a residency program, which typically lasts three years. Residency provides advanced training in foot and ankle surgery, as well as specialized care for complex conditions.
- Licensing: Podiatrists must pass a national licensing exam and meet state-specific requirements to practice in their area.
- Board Certification: While optional, some podiatrists choose to become board-certified by passing an additional exam that demonstrates expertise in the field.
Why Foot and Ankle Health Matters
However, they play an essential role in maintaining balance, mobility, and overall quality of life. Healthy feet are crucial for daily activities like walking, running, standing, and even sleeping. Without proper care, foot problems can lead to pain, disability, and a reduction in overall functionality.
Podiatrists are essential in preventing and treating conditions that can impact foot health, helping individuals stay mobile, active, and healthy throughout their lives. Early intervention and preventative care can greatly reduce the risk of serious complications, particularly for individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes or those who are active in sports or physical activities.
Conclusion
Podiatrists are specialized healthcare professionals who provide vital care for the feet, ankles, and lower extremities. Their expertise in diagnosing, treating, and preventing a wide range of conditions allows them to address the unique needs of their patients and ensure the best possible outcomes for foot health. Whether it’s managing chronic conditions, treating injuries, performing surgery, or providing preventative care, podiatrists are essential members of the healthcare community. Maintaining good foot health is crucial to overall well-being, and podiatrists help individuals stay mobile, pain-free, and active throughout their lives.